![]() EqapMacro (version 4.1syn, 11.03.2011)
EqapMacro (version 4.1syn, 11.03.2011)
EqapMacro (version 4.1syn, 11.03.2011)
The EqapMacro is a part of EqapPackage and is a functional component designed to create and execute the specially ordered text lines (macro). A macro can implement various arithmetical and algebraic calculations, use of functions and procedures, working with strings and arrays etc. The EqapMacro uses enhanced visual opportunity when a macro is created, edited or executed: syntax highlighting, quick command insertion, floating help for parameters of functions and procedures, text lines numbering, macro status line. This version of EqapMacro (4.1syn, 11.03.2011) uses SynMemo component as a text field (see http://synedit.sourceforge.net).
The EqapMacro implements the interactive user interface that allows (when an appropriate function or procedure has been correctly used) a message, a dialog window, or a chart diagram to be displayed, and to open and save macro files. The EqapMacro has the syntax-based text analyzer (parser) and the text-line interpreter. The text-line may contain any combination of numbers, strings, arithmetical/algebraic forms, functions, procedures, directives, constants and variables. An arbitrary nesting of the arithmetical/algebraic forms is allowed. The text interpreting is case-insensitive. A macro execution embodies: Appearance, structure and functionality of EqapMacro are described in detail in the following topics: 3. Basic text elements and commands The EqapMacro (Fig. 1) has control panel (a) and macro status line (b), main text field (c) and macro execution line (d). Fig. 1. The appearance of EqapMacro and an example of macro The control panel has buttons for quick operations with EqapMacro:
- the checking of each line for syntax consistency (see below);
- the creating of a list of variables;
- the checking of cycle blocks and condition blocks for consistency (see below);
- if the checking is OK, the line-to-line macro execution is started (for cycle-blocks, the corresponding lines are executing cyclically in the line-to-line manner);
- if an error was occurred in currently executed line (e.g., an invalid parameter was used or a variable was not declared), the macro execution stopped, the error line is highlighted, and the line number and error type are displayed;
- if no errors were found, an user gets the needed result that he(she) wrote as a macro.
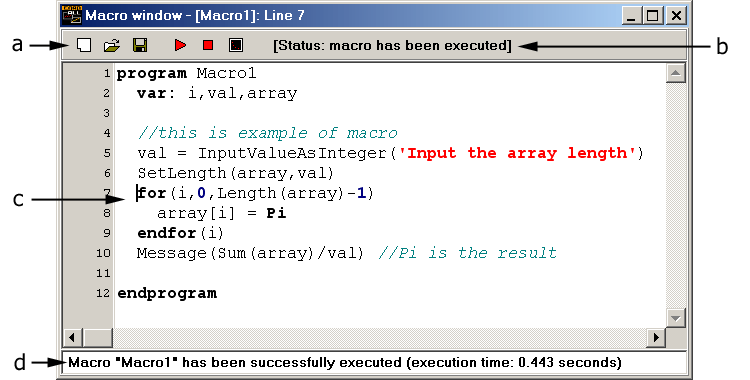
- clearance of the text field;
- loading a macro from file;
- saving a macro to file;
- starting a macro execution;
- stopping a macro execution;
- displaying a chart diagram used for series (if Chart: TChart is assigned, see below);
The macro status is displayed in the field (b) in Fig. 1. For instance, the macro status is "[Status: macro is executing]" when the macro is being executed; the macro status is "[Status: macro has been saved]" when the macro content has been saved recently.
The macro execution status is displayed in the field (d) in Fig. 1. This field contains a line number that is currently executed. When the macro execution is finished, this field contains the message of successful execution and time spent for this execution.
The main text field is used for filling of macro lines. By default, white background of the field and mono-spaced font Courier New are used. The syntax highlighting settings are editable. By default, keywords are highlighted with bold black, comments - with italic teal, string parameters - with bold red, numbers - with bold dark-blue (Fig. 2, a-d).
A list of functions, procedures, directives and constants is used to facilitate text typing; the combination of CTRL+Enter should be used for quick access to the drop-down list (Fig. 2, e). If the needed command is selected from the list, press Enter for quick "in-place" insertion of the command and closing of the list. Also, an auto-selection from the list is implemented for fast finding of the needed command. If the list is shown and focused, a typing of first symbol(s) of a command name scrolls the list to desired or resembled word. E.g., typing of "Co" scrolls the list and automatically selects CollapseArray function.
Fig. 2. Syntax highlighting and drop-down list of commands in EqapMacro
The floating hint would appear when an user types the name of a parametric function or procedure. This hint shows the parameter names and types (Fig. 3), and is appearing automatically either after selection of function or procedure from the drop-down list (e) in Fig. 2 or when the symbol "(" is typed after the name of function or procedure (if parametric). Typing the first parameter and comma (used as parameter separator) selects the next parameter with bold, and so on. The required (mandatory) parameters are displayed in the hint without any special selection (e.g., "Value: integer") whereas the optional (not mandatory) parameters are embraced with square brackets (e.g., "[From: integer]"). Press Esc to hide the floating hint.
Fig. 3. The floating hint in EqapMacro
The syntax used in EqapMacro resembles both Pascal and Microsoft Visual Basic and is case-insensitive. A single line is executed as complete expression. In any line, the expression should be complete with syntax (which is a prominent drawback of EqapMacro because you have to complete any long expression within single line). As well, any line is independent from others, except the lines used for program-endprogram structure, cycle block for(...)-endfor(...) or condition block if(...)-endif.
A macro consists of symbols and words, some of which have special purposes. The syntax highlighting facilitates the visual understanding and perception of macro text in EqapMacro. The text elements in macro are: keywords, variables, function, procedures, directives, constants, string expressions, comments and identifiers.
The identifiers are space symbol and symbols "()*+,-./:<=>[]". The comma is used for enumeration of parameters within functions and procedures, or array elements. The round brackets "()" are used for local operation identification and for identification of parameters within functions and procedures. The symbol "=" is used to equate with command result, and also used in condition block. The symbols ">" and "<" also used in the condition block. The square brackets "[]" are reserved for identification of array elements or indexed elements of objects.
The string parameter is a line part enclosed with symbols "'" (apostrophe) from left and right; by default, strings are highlighted in macro text with bold red font:
BuildCurve(X, Y, 'Title of this curve', clRed)
The comments are used to describe a line content and action, or to ignore temporarily the line part. As in IDE Delphi 6, the comment within a single line is the rest of the line following double slash ("//"). The comment block is the multi-line part of a macro located between "{" and "}".
3. Basic text elements and commands
Variables, if intended for direct using in a macro, might follow by the keyword var and are comma-separated. A variable used in macro is not necessarily should be declared in the var section. Nevertheless, you must declare a variable in this section if the variable is used in cycle block for or used as array variable in the corresponding functions and procedures, otherwise an error occurs (see "Macro execution errors"). The line with keyword var should follow the line with keyword program and a macro name. The EqapMacro reserves several variable types: vtInteger (an integer number), vtFloat (a number with floating point), vtString (a string), vtBoolean (a boolean type), vtColor (a color type), vtArray1D (one-dimensional array of integer or float numbers), vtArray2D (two-dimensional array of integer or float numbers), vtObject (indeterminate object). If the type of a variable is unknown, the variable is automatically assigned as indeterminate type (e.g., when a variable is an object). The examples of variables with different types are listed below:
n = 10 (integer number, vtInteger)
val = 0.25 (float number, vtFloat)
s = 'test' (string, vtString)
b = true (boolean type, vtBoolean)
clr = clRed (color type, vtColor)
mas1D = ValueArray[0] (one-dimensional array, vtArray1D)
mas2D = ValueArray[0][20] (two-dimensional array, vtArray2D)
obj = WindowCol[0].Group[0].Item[6] (the variable is object, vtObject)
Note that a variable name should not coincide with the name of functions, procedures, directives, constants or keywords.
Constants are the fixed names used as equivalents of the particular values. Variables are restricted to be used with the name reserved for constants. The EqapMacro reserves the names of following basic constants:
Pi - the Pi number.
false, true - the values of boolean type.
clAqua, clBlack, clBlue, clFuchsia, clGray, clGreen, clLime, clMaroon, clNavy, clOlive, clPurple, clRed, clSilver, clTeal, clWhite, clYellow - the values of "color" type.
mrCircle, mrCross, mrDiagCross, mrDiamond, mrDownTriangle, mrNone, mrRectangle, mrSmallDot, mrStar, mrTriangle - the types of series marker.
psClear, psDash, psDashdot, psDashdotdot, psDot, psInsideframe, psSolid - the types of series line.
ptDec, ptInc - "direction" types (decrease, increase).
etMax, etMean, etMin - the types of extremum.
atXAxis, atYAxis, atZAxis - the types of chart axis.
aotAdd, aotDivide, aotMultiply, aotSubtract - the types of arithmetic operation.
rtDecimalLogarithmic, rtExponent, rtExponential, rtExponentialWithSaturation, rtHyperbolic, rtLinear, rtNaturalLogarithmic, rtPolynomial, rtPower, rtSmolukFitting - the types of regression equation.
ftBasedOnPreviousValue, ftCubicSpline, ftFourier, ftGaussian, ftLinear3Points, ftLinear5Points, ftMovingAverage, ftMovingMedian, ftNonlinear7Points - the types of array smoothing algorithm.
amctRectangleNoRemainderTerm, amctRectangleWithRemainderTerm, amctTrapeziumNoRemainderTerm, amctTrapeziumWithRemainderTerm - the types of area calculation (for arrays).
Also, an user can add own constants in EqapMacro, both in Design-time and Run-time modes. User constant name should not coincide with existing names of constants, keywords, function, procedures and directives and must be followed by symbol "=" and a value of this constant (e.g., "myconst=0.523").
Keywords are used to indicate the special structures or special blocks in a macro text; some of the keywords are functions or directives. By default, the keywords are highlighted in macro text. The following keywords are reserved in EqapMacro:
program - indicates the beginning of macro; the macro text should start from this keyword followed by the macro name; used with endprogram.
endprogram - indicates the end of macro; used with program.
var - indicates the line with declared variables; the line with this keyword should follow the line with keywords program and a macro name.
integer - indicates the conversion to integer type, is a function.
string - indicates the conversion to string type, is a function.
boolean - indicates the conversion to boolean type, is a function.
if - indicates the beginning of condition block; used with endif, is a directive.
endif - indicates the end of condition block; used with if, is a directive.
for - indicates the beginning of cycle block; used with endfor, is a directive.
endfor - indicates the end of condition block; used with for, is a directive.
Directives are the special commands that may require parameter(s) and make some actions, but do not any calculations and do not return a result. Some directives are also the keywords, so these directives are highlighted in a macro text:
break(Variable): directive - the directive to break a current cycle and exit from cycle block for(Variable...)-endfor(Variable).
continue(Variable): directive - the directive to go to the next cycle of cycle block for(Variable...)-endfor(Variable).
endfor(Variable): directive - the directive of the end of cycle block for(Variable...)-endfor(Variable).
endif: directive - the directive of the end of condition block if(...)-endif.
for(Variable, From, To, [Step]): directive - the directive of the beginning of cycle block for(Variable...)-endfor(Variable).
if(set of conditions): directive - the directive of the beginning of condition block if(...)-endif.
Procedures and functions are the special names used to call the particular action(s) or calculation(s). Procedure or function might be non-parametric (does not require any parameter to be passed) or use required or optional (non-required) parameters. A procedure is the command that does not return any numerical result or value. In contrast, a function is the command which returns any result (a number or a value) to assigned variable. It is not allowed to use a variable with name of any function or procedure.
The functions and procedures may require or not require parameter(s). The parameters should be enclosed in round brackets that follow function/procedure name; the comma is used for parameters enumeration. The parameter might be required or optional. If the required parameter is omitted, a macro execution error occurs. If optional parameter is omitted then no error appears because EqapMacro invisibly uses the default values for optional parameters. The required parameters are presented (for instance, in the text of floating hint) in an usual manner (e.g., "Value: integer") whereas the optional are enclosed with square brackets (e.g., "[From: integer]").
The standard set of procedures and functions in EqapMacro covers all that you need to make widespread mathematical calculations, to work with 1-D and 2-D numerical arrays as well as with string data, to use the interactive possibilities by working with dialog boxes, and to build the graphical data. The procedures and function, divided by the categories, are listed below and have a brief description. Arrays or array-organized objects are indexed from 0, if not stated otherwise.
Type conversion functions
boolean(Value): function - converts Value (integer) to boolean type (vtBoolean).
integer(Value): function - converts Value (integer or float) to integer type (vtInteger).
string(Value): function - converts Value (integer or float) to string type (vtString).
The procedures and functions for mathematical calculations
NOTE: if not stated otherwise, in the listed commands the parameter From (integer) is an index (of array) to start the requested operation, Count (integer) is a number of array elements used for the operation.
Abs(Value, [From], [Count]): function - returns the absolute of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
CalcArea(X, Y, Method, BindToZero, [From, Count]): function - returns the area value, calculated for a curve with X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions). Method (constant) indicates the area calculation type (amctRectangleNoRemainderTerm - rectangles without remainder term, amctRectangleWithRemainderTerm - rectangles with remainder term, amctTrapeziumNoRemainderTerm - trapeziums without remainder term, amctTrapeziumWithRemainderTerm - trapeziums with remainder term). BindToZero (vtBoolean) indicates whether the initial X- and Y-values should be shifted to "0".
CalcAutoCorrelation(Array): function - returns the value of autocorrelation function of Array (one- or two-dimensional array).
CalcCrossCorrelation(Array1, Array2): function - returns the value of cross-correlation function of Array1 and Array2 (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions).
CalcDerivative(X, Y, [From], [Count]): function - returns the derivative of Y (one- or two-dimensional array) calculated for argument X (integer or float).
CalcEquation(X, EquationType, EquationCoefficients): function - returns the equation value, calculated by the X (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array). EquationType (constant) indicates the regression equation type (rtDecimalLogarithmic - decimal logarithmic function y = C1Log10(x) + C0, rtExponent - power function y = C2(C1x) + C0, rtExponential - exponential function y = C2exp(C1x) + C0, rtExponentialWithSaturation - exponential function with saturation y = C2(1 - exp(C1x)) + C0, rtHyperbolic - hyperbolic function y = C1/x + C0, rtLinear - linear function y = C1x + C0, rtNaturalLogarithmic - natural logarithmic function y = C1Ln(x) + C0, rtPolynomial - polynomial function yn = Cnxn + Cn-1xn-1 + ... + C1x + C0, rtPower - power function y = C2xC1 + C0, rtSmolukFitting - function y = (C2 - C0)exp(C1√x) + C0). EquationCoefficients (one-dimensional array) specifies the equation coefficients. As example, if Coefs is an array of two values (2,0.5), the result of calculation of macro string "y = CalcEquation(10,rtLinear,Coefs)" is "7" (calculated from Coefs[1]*10 + Coefs[0]).
CalcPolynomialRegressionCoefficients(X, Y, [PolynomialDegree]): function - returns the coefficients of polynomial regression of X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions). PolynomialDegree (integer) indicates the polynomial degree (the default value is "3"). The coefficients of polynomial regression are indexed from 0; the indexing order conforms with equation yn = Cnxn + Cn-1xn-1 + ... + C1x + C0.
CalcPolynomialRegressionRSquare(X, Y, [PolynomialDegree]): function - returns R2 (the determination coefficient) for polynomial regression of X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions). PolynomialDegree (integer) indicates the polynomial degree (the default value is "3").
CalcRegressionCoefficients(X, Y, RegressionType, [Corrector]): function - returns the coefficients of regression (with specified type) of X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions). RegressionType (constant) indicates the regression type (see CalcEquation). Corrector (integer or float, should be >0) is a correcting coefficient (the default value is "0"). The coefficients of specified regression are indexed from 0; the indexing order conforms with equation of the selected regression.
CalcRegressionRSquare(X, Y, RegressionType, [Corrector]): function - returns R2 (the determination coefficient) for specified regression of X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions). RegressionType (constant) indicates the the regression type (see CalcEquation). Corrector (integer or float, should be >0) is a correcting coefficient (the default value is "0").
Cos(Degree, [From], [Count]): function - returns the cosinus of Degree (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array); the parameter should be expressed as degree.
Dec(Variable): procedure - decreases (by 1) the value of Variable (integer).
Dispersion(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the dispersion of Array (one- or two-dimensional array).
DispersionError(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the dispersion error of Array (one- or two-dimensional array).
Even(Value): function - returns "1" if Value (integer) is even, "0" - if odd.
Exp(Value, [From], [Count]): function - returns the exponent of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
Factorial(Value): function - returns the factorial of Value (integer).
GeometricAverage(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the geometric average of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
GetExtremum(Array, ExtremumType, [From], [Count]): function - returns the extremum of Array (one- or two-dimensional array). Extremum (constant) indicates the extremum type (etMax - maximum, etMean - arithmetic average, etMin - minimum).
HarmonicAverage(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the harmonic average of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Inc(Variable): procedure - increases (by 1) the value of Variable (integer).
Ln(Value, [From], [Count]): function - returns the natural logarithm of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
Log(Value, Base, [From], [Count]): function - returns the decimal logarithm of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
Max(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the maximum of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Mean(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the arithmetic average of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Median(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the median of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
MedianError(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the median error of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Min(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the minimum of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Odd(Value): function - returns "1" if Value (integer) is odd, "0" - if even.
Power(Value, Exponent, [From], [Count]): function - returns the arbitrary power of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array), where the power is Exponent (integer or float).
PowerAverage(Array, Power, [From], [Count]): function - returns the power average of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Random(Range): function - returns the random number between 0 and Range-1 (Range is integer). You need to call Randomize prior to proper using this function.
Randomize: procedure - enables the mode of random number generation.
Sin(Degree, [From], [Count]): function - returns the sinus of Degree (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array); the parameter should be expressed as degree.
Sqr(Value, [From], [Count]): function - returns the square power of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
Sqrt(Value, [From], [Count]): function - returns the square root of Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
StdDev(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the standard deviation of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Sum(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the sum of elements of Value (one- or two-dimensional array).
Trunc(Value, [From], [Count]): function - returns the truncated Value (integer, float, one- or two-dimensional array).
Numerical array-related procedures and functions
NOTE: if not stated otherwise, in the listed commands the parameter From (integer) is an index of array to start the requested operation, Count (integer) is a number of array elements used for the operation.
CollapseArray(Array, CollapseCoef, [From], [Count]): function - returns the array resulted by the specific deletion of elements from Array (one- or two-dimensional array). CollapseCoef (integer) sets the "collapsing" coefficient. If CollapseCoef is 0 then the resulting array is the same as Array. If CollapseCoef is 1, the resulting array consists of first, third, fifth etc. elements of Array (that is, every next element is ignored). If CollapseCoef is 2, the resulting array consists of first, fourth, seventh etc. elements of Array (every two next elements are ignored). The universal rule to select an element is that the resulting array will consist elements with 0-index and with any index divisible by (CollapseCoef+1). E.g. if Array is (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9), the line CollapseArray(Array,2) returns the array (0,3,6,9).
CopyArray(Array, [From], [Count]): function - returns the array of values copied from Array (one- or two-dimensional array).
DefineArray(Set of values): function - returns the array of values enumerated by the comma. E.g., DefineArray(2,4,6) returns the array of three elements with the corresponding values.
DeleteArray(Array, From, Count): function - returns the array resulted by the deletion of elements from Array (one- or two-dimensional array).
ExpandArray(Array, ExpandCoef, [From], [Count]): function - returns the array resulted by the specific addition of elements to Array (one- or two-dimensional array). ExpandCoef (integer) sets the number of elements that should be added between any two neighbour elements of Array. If ExpandCoef is 0 then the resulting array is the same as Array. If ExpandCoef is 1, the resulting array consists of elements from Array with one new element being inserted between any two neighbour points; the number of elements in the resulting array is twofold number of Array elements minus 1. If ExpandCoef is 2, the resulting array consists of elements from Array with two new elements being inserted between any two neighbour points; the number of elements in the resulting array is threefold number of Array elements minus 2. The universal rule to calculate the number of elements in the resulting array is Length(Array)*(ExpandCoef+1)-ExpandCoef. The new elements inserted between existing elements are not zeroed. Instead, the values are intermediate between the existing values, and these values are calculated on the basis of linear interpolation. E.g. if Array is (0,1,2), the line ExpandArray(Array,1) returns the array (0,0.5,1,1.5,2).
FilterArray(Array, FilterType, Discret, SplitCoef, ExpandCoef, IsCycled): function - returns the array resulted by a smoothing of data in Array (one- or two-dimensional array). FilterType (constant) indicates the smoothing algorithm type (ftBasedOnPreviousValue - smoothing by previous values, ftCubicSpline - smoothing by cubic splines, ftFourier - smoothing by Fourier harmonics, ftGaussian - smoothing by Gaussian method, ftLinear3Points - linear smoothing by 3 points, ftLinear5Points - linear smoothing by 5 points, ftMovingAverage - smoothing by moving average, ftMovingMedian - smoothing by moving median, ftNonlinear7Points - nonlinear smoothing by 7 points). Discret (integer, should be >0) sets the "time" interval and used for smoothing by cubic splines only. SplitCoef and ExpandCoef (integer) and IsCycled (boolean type, vtBoolean) indicates the parameters of selected smoothing algorithm (see EqapMath for details).
GetPointCountAboveLevel(Array, Level): function - returns the number of points in Array (one- or two-dimensional array) with a value that higher than Level (integer or float).
GetPointCountBelowLevel(Array, Level): function - returns the number of points in Array (one- or two-dimensional array) with a value that smaller than Level (integer or float).
GetValueIndex(Array, Value, [From], [Count], [FindNearest]): function - returns the index of point in Array (one- or two-dimensional array), which value is equal to Value (integer or float). If the Array contains several points with Value, the function result is first index. FindNearest (vtBoolean) indicates whether the function should find the point with exact or nearest value.
InsertArray(Array, InsertedArray, From): function - returns the array where the values of InsertedArray (one- or two-dimensional array) are inserted into Array (one- or two-dimensional array). From (integer) is an index of Array from which the values of InsertedArray are inserted.
Length(Array): function - returns the length (number of elements) of Array (one- or two-dimensional array). The result is either integer value if Array is one-dimensional or array of two values if Array is two-dimensional (matrix). In latter case, the first value is a high-order dimension of Array and second value is a low-order dimension of Array.
SetLength(Array, Length1, [Length2]): procedure - creates the array of specified number of elements (all are equal to 0). Array should be a variable declared in var section. If Length1 (integer) is the only parameter, the result is one-dimensional array of Length1 elements. If Length2 (integer) is also used, the result is two-dimensional array (matrix) where the high-order dimension is Length1 and low-order dimension is Length2.
ShiftArray(Array, ShiftType, ShiftValue, Circled): function - returns the array resulted by the shifting of elements of Array (one- or two-dimensional array). ShiftType (constant) indicates the shifting direction (ptDec - to the first element, ptInc - to the last element). ShiftValue (integer) indicates the number of shift steps. Circled (boolean type, vtBoolean) indicates whether the shifting should be looped (the first/last element is moved to the opposite end of array. E.g., Array is (0,1,2,3,4). The line ShiftArray(Array,ptInc,2,true) returns the array (3,4,0,1,2), due to the looped shifting. The line ShiftArray(Array,ptInc,2,false) returns the array (0,0,0,1,2), due to the unlooped shifting where elements Array[3] and Array[4] are zeroed.
SortArray(Array, SortType): procedure - sorts the values of Array (one- or two-dimensional array). SortType (constant) indicates the sorting direction (ptDec - by decrease, ptInc - by increase).
SortLinkedArrays(SortingArray, LinkedArray, SortType): procedure - sorts the values of SortingArray and LinkedArray (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions). The sorting is doing for SortingArray, whereas the values of LinkedArray are rearranged on the relation with this sorting (linked sorting). SortType (constant) indicates the sorting direction (ptDec - by decrease, ptInc - by increase).
TurnArray(Array): function - returns the array in which the elements of Array (one- or two-dimensional array) are rearranged in the reverse order. E.g., for source Array (1,2,3) the function returns an array (3,2,1).
String-related procedures and functions
ConcatenateString(String1, String2, ...): function - returns the string variable that is concatenation of String1, String2 etc.
CopyString(SourceString, [From], [Count]): function - returns the string variable copied from SourceString. From is an index of symbol in SourceString used to start the copying (integer, indexing from 0). Count (integer) is a number of symbols to be copied.
DeleteString(SourceString, [From], [Count]): function - returns the string variable resulted by the deletion of symbols from SourceString. From is an index of symbol in SourceString used to start the deletion (integer, indexing from 0). Count (integer) is a number of symbols to be deleted.
InsertString(SourceString, InsertedString, From): function - returns the string variable resulted in the insertion of InsertedString into SourceString. From is an index of symbol in SourceString used to start the insertion (integer, indexing from 0).
IsSubstringExists(SourceString, Substring, [CaseSensitive]): function - returns "true" if SubString is existing in SourceString, or "false" if SubString is not found. CaseSensitive (boolean type, vtBoolean) indicates whether letter case should be taken into account or not.
LowerCaseString(String): function - returns the string variable where all symbols of String are lowercased.
NumToStr(Value, [DigitsAfterSeparator]): function - converts Value (integer or float) to a string variable. DigitsAfterSeparator (integer) indicates how many digits should be used in the resulting string if a float number is converted (the default value is "3").
ReplaceString(SourceString, FindString, ReplaceString, [ReplaceAll]): function - returns the string variable where FindString (substring of SourceString) is replaced by ReplaceString (all three parameters are strings). ReplaceAll (boolean type, vtBoolean) indicates whether all FindString should be replaced or the first occurrence of FindString only.
StrToNum(Value): function - converts Value (string type, vtString) to a number.
UpperCaseString(String): function - returns the string variable where all symbols of String are uppercased.
Diagram-related procedures and functions
NOTE: if not stated otherwise, the the listed commands the parameter Title is a series title (vtString), Color - a series color (vtColor, see "Constants"), LineStyle - a series line style (psClear - no line, psDash - dashed line, psDashdot - dash-dot line, psDashdotdot - dash-dot-dot line, psDot - dotted line, psInsideframe - "flickered" line, psSolid - standard line), LineWidth - a series line width (integer), MarkerStyle - a series marker style(mrCircle - circled marker, mrCross - crossed marker, mrDiagCross - diagonally crossed marker, mrDiamond - diamond marker, mrDownTriangle - downside triangle marker, mrNone - no marker, mrRectangle - rectangle marker, mrSmallDot - small dots, mrStar - asterisk, mrTriangle - upside triangle marker, MarkerSize - a series marker size (integer).
AddPoint(SeriesIndex, X, Y): procedure - adds a point with X and Y-values (integer or float) to the created series of Chart (property of EqapMacro) with index SeriesIndex (indexing from 0).
AutoSelectColor: procedure - enables the color autoselection mode, when working with a series.
BuildCurve(X, Y, [Title], [Color], [LineStyle], [LineWidth]): procedure - builds the linear curve without markers, using Y-values (one- or two-dimensional array) and increment X (integer or float).
BuildDistribution(Array, IntervalCount, [Title], [Color], [MarkerStyle], [MarkerSize], [LineStyle], [LineWidth]): procedure - builds the distribution diagram of Array (one- or two-dimensional array) with the numbers of interval is equal to IntervalCount (integer).
BuildLineRelation(X, Y, [Title], [Color], [LineStyle], [LineWidth]): procedure - builds the linear curve without markers, using X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions).
BuildPhasePortrait(X, Y, [Title], [Color], [MarkerStyle]): procedure - builds the "phase portrait" (only points with no lines between) using X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions).
BuildPointRelation(X, Y, [Title], [Color], [MarkerStyle], [MarkerSize], [LineStyle], [LineWidth]): procedure - builds the linear curve with markers, using X- and Y-values (one- or two-dimensional arrays with equal dimensions).
BuildPolynomialRegressionCurve(SeriesIndex, PolynomialDegree, [Title], [Color], [MarkerStyle], [MarkerSize], [LineStyle], [LineWidth]): procedure - builds the linear curve with markers and fills the curve with values calculated on the basis of polynomial regression equation, using X- and Y-values from the specified series with index SeriesIndex (indexing from 0). PolynomialDegree indicates the polynomial degree.
BuildRegressionCurve(SeriesIndex, RegressionType, [Corrector], [Title], [Color], [MarkerStyle], [MarkerSize], [LineStyle], [LineWidth]): procedure - builds the linear curve with markers and fills the curve with values calculated on the basis of specified regression equation, using X- and Y-values from the specified series with index SeriesIndex (indexing from 0). RegressionType (constant) indicates the regression type (see CalcEquation). Corrector (integer or float, should be >0) is a correcting coefficient (the default value is "0").
ClearDiagram: procedure - clears the content of Chart (property of EqapMacro).
DeletePoint(SeriesIndex, From, Count): procedure - deletes the points from series of Chart (property of EqapMacro) with index SeriesIndex (indexing from 0). From is an index of series to start the deletion (indexing from 0). Count is a number of points used for the deletion (integer).
ShowDiagram: procedure - displays the window which is a parent window of Chart (TChart).
Dialog-related procedures and functions
ExecuteColorDialog: function - displays the dialog to set the value of "color" variable (vtColor).
InputValueAsBoolean([PromptString]): function - displays the dialog to set the value of logical variable (vtBoolean).
InputValueAsFloat([PromptString]): function - displays the dialog to set the value of float number (vtFloat).
InputValueAsInteger([PromptString]): function - displays the dialog to set the value of integer number (vtInteger).
InputValueAsObject([PromptString]): function - displays the dialog to set the value of unidentified variable (vtObject).
InputValueAsString([PromptString]): function - displays the dialog to set the value of string variable (vtString).
Message(Value: any): procedure - displays the message that contains any text or string equivalent of a number (vtInteger ��� vtFloat), one-dimensional array (vtArray1D) or two-dimensional array (vtArray2D). If an arithmetic expression is passed as the parameter Value, the procedure returns both text expression and result of calculation of this expression. E.g., the line "Message(2+3)" will display the message "2+3 = 5".
ShowRegressionEquation(RegressionType): procedure - displays the standard form of specified regression equation. RegressionType (constant) is a regression type (see CalcEquation). E.g., for linear regression (rtLinear) the procedure will display the message "y = C(1)*x + C(0)".
Service procedures and functions
StopExecution: procedure - stops the execution of a macro.
Other procedures and functions
InvertColor(Color): function - returns the inverted value of Color (color type, vtColor).
RGBToColor(RedValue, GreenValue, BlueValue): function - returns the "color" variable (vtColor) resulted by a mixing of three RGB values RedValue, GreenValue and BlueValue (integer between 0 and 255).
SaveToFile(FileName, Value): procedure - saves Value (string data, variables, numbers, or arrays) to the file with name FileName.
4. Extending of the basic functionality
The list of standard procedures and functions of EqapMacro may be extended by an user, in Design-time and Run-time modes. This allows the functional possibilities of EqapMacro to be increased significantly. However, to do this you have not only to add manually a new function/procedure name and its parameters. More important, you have to complete the specific code in your EqapMacro-inherited component, developed in the IDE Delphi 6. The example below illustrates the necessary two actions of an user.
To demonstrate the manual addition of your own procedures and functions to the standard EqapMacro functionality, run the IDE Delphi 6 and create a new application project (File -> New -> Application); put new TEqapMacro component (named EqapMacro1 by default) from component palette to your new empty form. Select EqapMacro1 to display its properties in Object Inspector; find and select MacroSyntax -> Procedures (TStringList) to open the string editor window. You may add new strings with correct syntax. If new function or procedure is non-parametric (does not use any parameter), please adhere the following syntax: function/procedure name, colon, the word to identify type of new command [procedure or function]. If new function or procedure is parametric (does require parameters), please adhere the following syntax: function/procedure name, the names of parameters listed by the comma and enclosed within round brackets, colon, the word to identify type of new command [procedure or function]. Names of optional parameters should be enclosed in square brackets, e.g. "MyProcedure(Param1, [Param2])". You may use spaces to facilitate the visual understanding of string lines. The example of new string lines with correct syntax is below:
Procedure1: procedure;
Procedure2(NumValue, StrValue): procedure
Function3(Value, Array): function
Close the string editor window. EqapMacro can distinguish now these new names as function or procedure name; moreover, the names appear in the drop-down list of commands (when CTRL+Enter is pressed). The next is to learn EqapMacro to display the floating hint with the parameters of these new functions and procedures. Find and select MacroSyntax -> HelpStrings (TStringList) in the Object Inspector. Add new strings to the string editor window, using a correct syntax. Course, you have to add new string for the help content of function/procedure only if it uses parameters. Adhere the following syntax: function/procedure name, vertical bar (|), name of first parameter, colon, type of first parameter, vertical bar, name of second parameter, colon, type of second parameter, vertical bar, etc. The possible parameter types are: integer (integer number, vtInteger), float (float number, vtFloat), string (vtString), boolean (boolean type, vtBoolean), color (vtColor), array (one- or two-dimensional array, type vtArray1D and Array2D, respectively), object (unidentified type, vtObject). Several types may be used for a parameter type, e.g. "integer, float or boolean". The parameter description (name and type) should be enclosed in square brackets in case of use as optional, e.g. "MyProcedure|Param1: integer|[Param2: float]|". The example of new help string lines with correct syntax is below:
Procedure2|NumValue: integer or float|StrValue: string|
Function3|Value: integer or float|Array: array|
The EqapMacro is able now to distinguish and describe (for an user) the new functions and procedures as well as their parameters. However, when executing a new name, EqapMacro does not perform any action or calculation yet. This stage is only made a manual addition of new function/procedure name and description, with no any functional extending of EqapMacro. The next what is you need is to change the code of your Unit1 (of your application), in order to implement the necessary response of EqapMacro to the new function and procedure names. Figure 4 explains these code interventions (the code is downloadable as a zip-archive here):
Fig. 4. The example of code that implements an extension of EqapMacro functionality by the addition of new functions and procedures
As the result of described manual addition and programming, EqapMacro is able now to correctly interpret the new functions and procedures in a macro text (Fig. 5):
Fig. 5. The example of use of new functions and procedures, added by an user in EqapMacro
The EqapMacro inherits properties and events of TPanel except those used for text appearance (Alignment, AutoSize, Caption, Font etc.), and has own properties and events:
Properties
Chart: TChart - the chart used for series displaying. This property should be assigned (in Design-time or Run-time mode) prior to using of function and procedures that work with series.
ExecuteKey: TShortCut - the hotkey to start a macro execution. The default value is F9.
HelpKey: TShortCut - the hotkey to show help file. The default value is F1.
MacroName: string - the macro name. In general, does not coincide with the name of macro file.
MacroSyntax: TEqapMacroSyntax - the macro syntax. The following subproperties are existed: Constants: TStringList (not editable list of standard constants), HelpStrings: TStringList (editable list of hints for procedures and functions), KeyWords: TStringList (editable list of keywords), LineComment: string (symbol(s) used to indicate the start of comment line), MultiCommentLeft: string (symbol(s) used to indicate the start of comment block), MultiCommentRight: string (symbol(s) used to indicate the end of comment block), Procedures: TStringList (editable list of procedures and functions), Syntax: TSynGeneralSyn (this class is created by the SynMemo developers, seehttp://synedit.sourceforge.net) - the description of basic syntaxic rules of EqapMacro, UserConstants: TStringList (editable list of user constants).
Memo: TSynMemo - the visual settings of EqapMacro text field (SynMemo component, see http://synedit.sourceforge.net).
ModifiedCaption: string - the text that appears in title bar of the form which contains EqapMacro component. This text is followed by the name of active macro.
Options: TEqapMacroOptions - the EqapMacro options. Contains two options: emoModifyOwnerCaption (if true, the EqapMacro can change title bar text of the parent form), emoShowOwnToolbar (if true, the EqapMacro displays the control panel with quick operation buttons).
Events
OnAfterExecute: TNotifyEvent - event arises after the end of successful macro execution.
OnAfterOpenMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises after a macro file opening.
OnAfterSaveMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises after a macro file saving.
OnBeforeExecute: TNotifyEvent - event arises prior to macro execution.
OnBeforeOpenMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises prior to a macro file opening.
OnBeforeSaveMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises prior to a macro file saving.
OnCallHelp: TNotifyEvent - event arises just when the Help hot-key is pressed.
OnClearMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises after a macro text complete clearance.
OnExecuteError: TNotifyEvent - event arises just when an error execution is appeared.
OnCreateMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises just after creation of EqapMacro component.
OnDestroyMacro: TNotifyEvent - event arises just before destroying the EqapMacro component.
OnMemoKeyDown: TKeyEvent - event arises when any key is pressed down and the focus is in the text field of EqapMacro.
OnMemoKeyPress: TKeyPressEvent - event arises when any key is pressed and the focus is in the text field of EqapMacro.
OnMemoKeyUp: TKeyEvent - event arises when any key, that has been pressed before, is released and the focus is in the text field of EqapMacro.
In the case of error during the macro execution, EqapMacro selects the line with error occurred and displays possible reason of the error in macro execution line (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6. The visual information about an error occurred during the macro execution in EqapMacro
The following list contains the macro execution errors declared in EqapMacro:
"There are unpaired brackets of " - unclosed brackets of the specified type are found.
"Invalid syntax of function " - the function with specified name has invalid syntax.
"Invalid syntax of procedure " - the procedure with specified name has invalid syntax.
"Invalid syntax of " - the specified expression has invalid syntax.
"Incompatible arrays" - the parameters of function or procedure are arrays with unequal dimensions.
"Invalid parameter(s)" - parameter(s) used for function or procedure are invalid.
"Invalid parameter " - the specified parameter used for function or procedure is invalid.
"Inapplicable regression" - the specified regression type is inapplicable.
"Incomparable parameters " - the specified parameters are incomparable.
"Variable is not in varlist" - the specified variable is not declared in the list of variables (var list).
"Parameter is not array " - the specified parameter is not an array.
"Invalid index of array" - invalid array index is used.
"The directive not found" - no specified directive name was found.
"Zero or negative values are found" - zero or negative values found when calculation performed.
"Parameter is not COLOR property " - the specified parameter is not vtColor.
"Can''t build a series because DefaultChart is unassigned." - DefaultChart property is not assigned, the series cannot be created.
"Execution stopped by macro command." - the macro execution stopped due to StopExecution command.
"Unknown function, procedure, directive or variable name " - the specified name is not the name of function, procedure, directive or variable.
"Too many parameters used in " - too many parameters are used in the specified function or procedure.
"There are unpaired apostrophes" - unpaired apostrophe is found (this is used to identify the string constant).
"Variable name is empty" - the specified variable has not name.
"Variable name is duplicated" - the name of specified variable is already used.
"Variable name coincides with function, procedure, directive or constant name" - the name of specified variable coincides with the existing name of function, procedure, directive, or constant.
"A variable has to be assigned to take result of function " - a variable should be used to equate with the specified function result.
The examples of macro will be available in the next future.
All the software products are free for use. Any commercial using is not permitted without author's permission (o.lookin@iip.uran.ru).